Table of Contents
- Basic Facts
- Overview
- Data Wrangling and Data Cleaning
- Exploratory Data Analysis/Data Storytelling and Visualization
- Conclusion
- References
Basic Facts
HIV/AIDS Also called: human immunodeficiency virus, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
Global HIV & AIDS statistics — Fact sheet
According to UNAIDS:
Global HIV statistics
38.4 million [33.9 million–43.8 million] people globally were living with HIV in 2021. 1.5 million [1.1 million–2.0 million] people became newly infected with HIV in 2021. 650 000 [510 000–860 000] people died from AIDS-related illnesses in 2021. 28.7 million people were accessing antiretroviral therapy in 2021.
84.2 million [64.0 million–113.0 million] people have become infected with HIV since the start of the epidemic.
40.1 million [33.6 million–48.6million] people have died from AIDS-related illnesses since the start of the epidemic.
People living with HIV
In 2021, there were 38.4 million [33.9 million–43.8 million] people living with HIV.
36.7 million [32.3 million–41.9 million] adults (15 years or older).
1.7 million [1.3 million–2.1 million] children (0–14 years).
54% of all people living with HIV were women and girls.
85% [75– 97%] of all people living with HIV knew their HIV status in 2021.
About 5.9 million people did not know that they were living with HIV in 2021.
New HIV infections
New HIV infections have been reduced by 54% since the peak in 1996.
In 2021, around 1.5 million [1.1 million–2.0 million] people were newly infected with HIV, compared to 3.2 million [2.4 million–4.3 million] people in 1996.
Women and girls accounted for 49% of all new infections in 2021.
Since 2010, new HIV infections have declined by 32%, from 2.2 million [1.7 million–2.9 million] to 1.5 million [1.1 million–2.0 million] in 2021.
Since 2010, new HIV infections among children have declined by 52%, from 320 000 [220 000–480 000] in 2010 to 160 000 [110 000–230 000] in 2021.
Overview
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an infection that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the white blood cells called CD4 cells. HIV destroys these CD4 cells, weakening a person’s immunity against opportunistic infections, such as tuberculosis and fungal infections, severe bacterial infections and some cancers. It is spread by contact with certain bodily fluids of a person with HIV, most commonly during unprotected sex (sex without a condom or HIV medicine to prevent or treat HIV), or through sharing injection drug equipment.
If left untreated, HIV can lead to the disease AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
The human body can’t get rid of HIV and no effective HIV cure exists. So, once you have HIV, you have it for life. HIV causes AIDS and interferes with the body's ability to fight infections. The virus can be transmitted through contact with infected blood, semen or vaginal fluids. Within a few weeks of HIV infection, flu-like symptoms such as fever, sore throat and fatigue can occur. Then the disease is usually asymptomatic until it progresses to AIDS. AIDS symptoms include weight loss, fever or night sweats, fatigue and recurrent infections. No cure exists for AIDS, but strict adherence to antiretroviral regimens (ARVs) can dramatically slow the disease's progress as well as prevent secondary infections and complications. This project on HIV/AIDS covers three(3) countries in Africa, namely Nigeria, Cameroun and Côte d'Ivoire, and it provides insight analysis on Infected Demographic by Sex, Infected Demographic by age range, Reported cases by date, Affected locations heatmap, Mortality by region, Mortality by age range, etc. The dataset was gotten and compiled from vizhub.healthdata.org.
Data Wrangling and Data Cleaning
The dataset was cleaned and transformed using the Power Query Editor in PowerBI. Initially we separated the Mortality table from the Incidence table using Excel before we moved to power query editor where datatypes were changed, some columns removed and renamed and null values were replaced with zero.
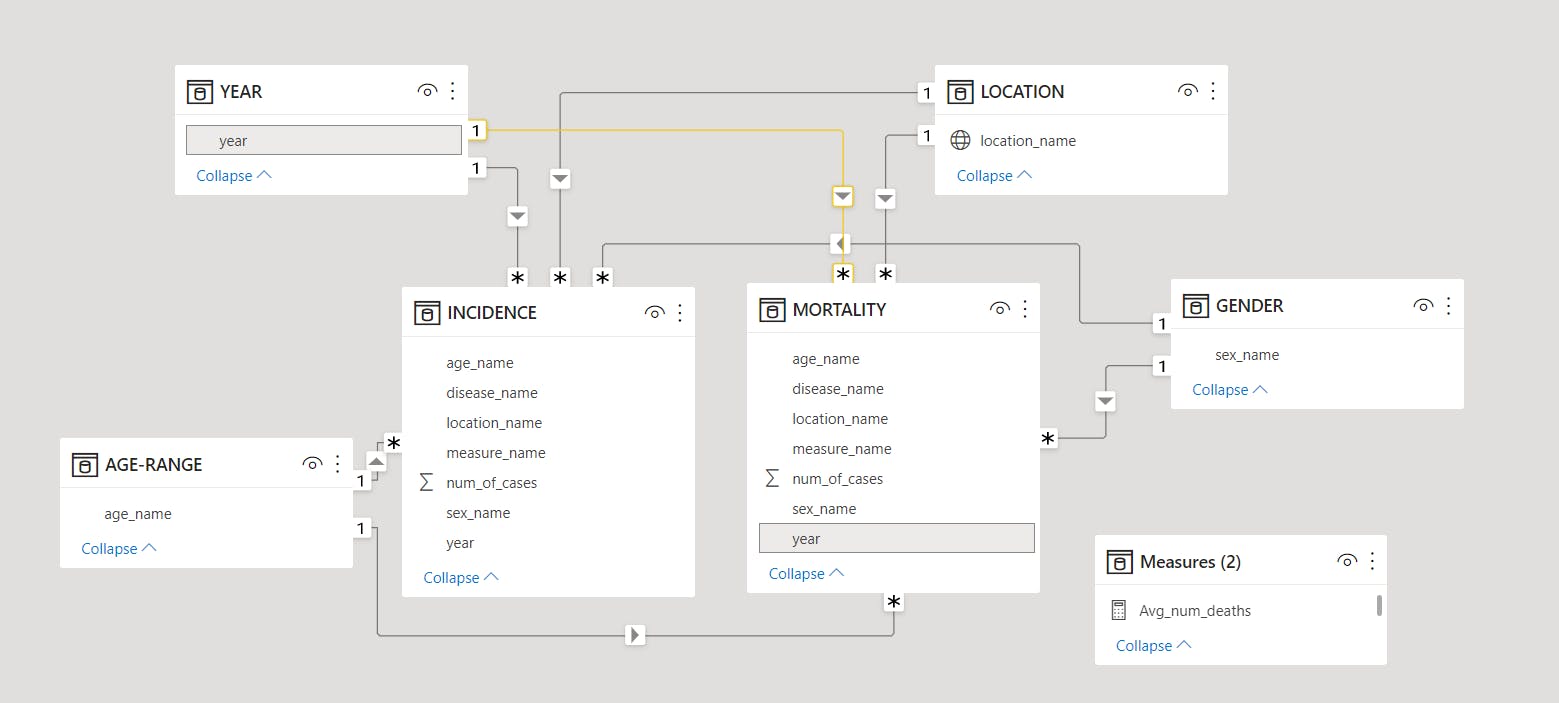
Relationships were created.
Exploratory Data Analysis/Data Storytelling and Visualization
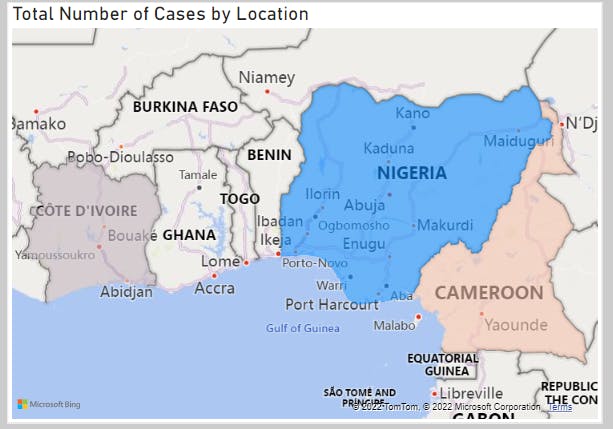
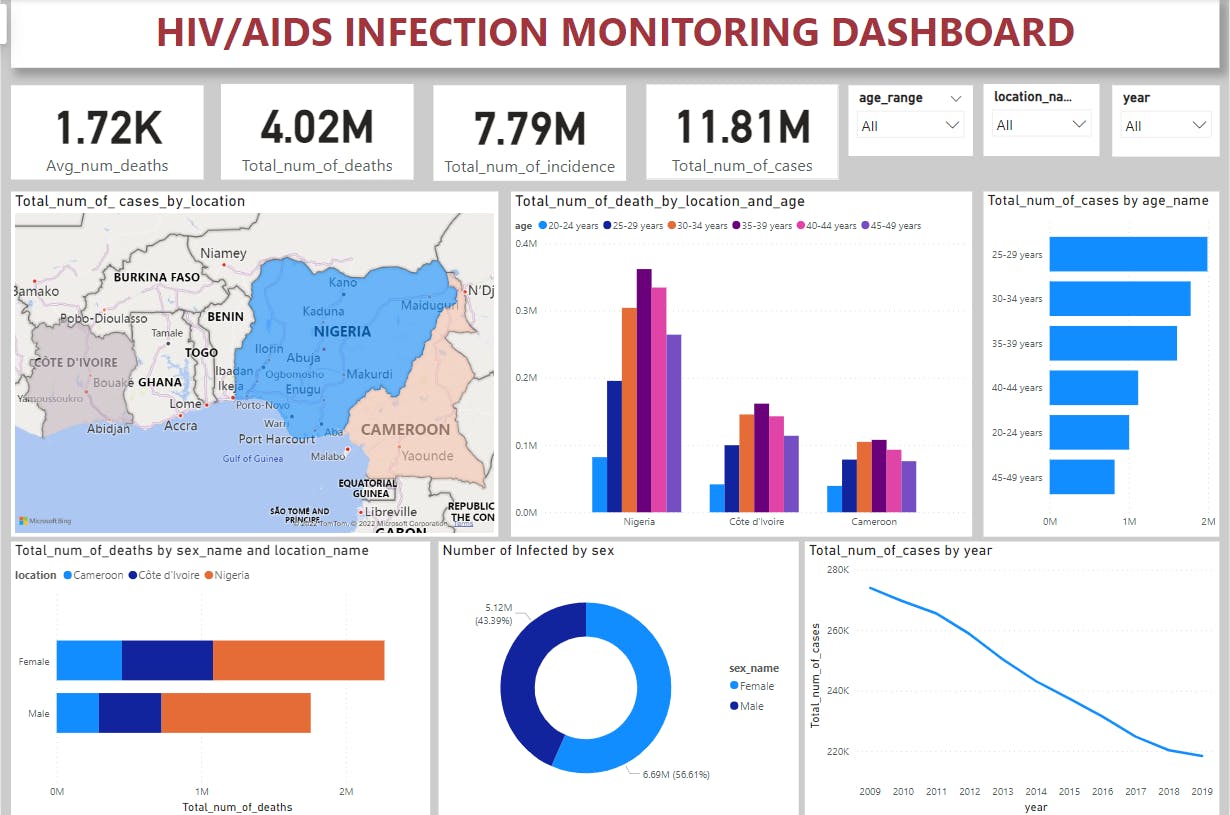
Analysis 1(Total Number of Cases by Location)
This shows the countries affected by HIV/AIDS that we are basing our studies and analysis on and shows Nigeria with the highest number of cases(6,837,065)
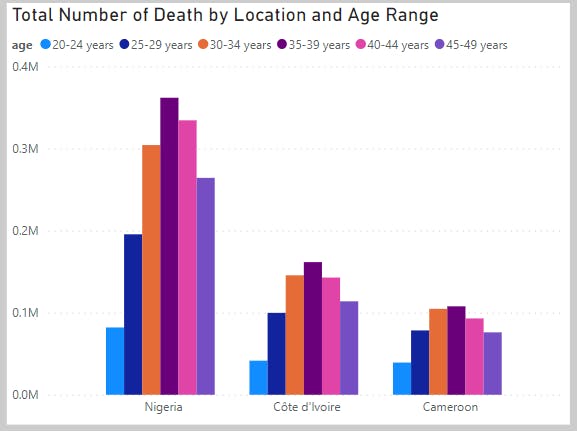
Analysis 2(Total Number of Death by Location and Age Range)
This analysis shows Nigeria being the location with the highest number of death(about 361,812 deaths) coming from the age range of 35-39 years.
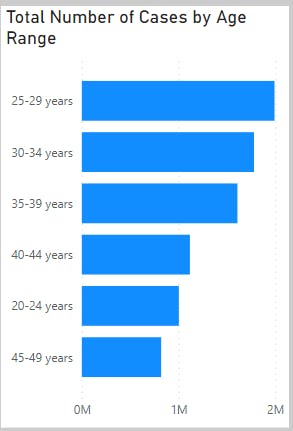
Analysis 3(Total Number of Cases by Age Range)
This analysis reveals age 25-29 years with the highest total number of HIV/AIDS cases.
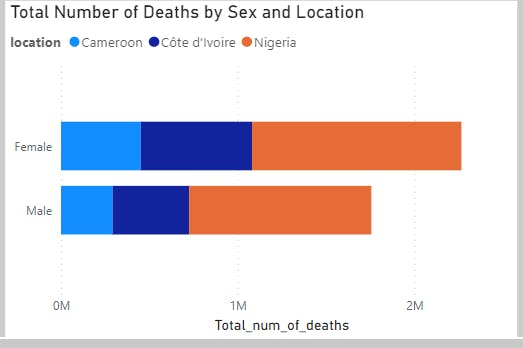
Analysis 4(Total Number of Deaths by Sex and Location)
This reveals Female sex with the highest number of deaths and in Nigeria as compared to Male sex.
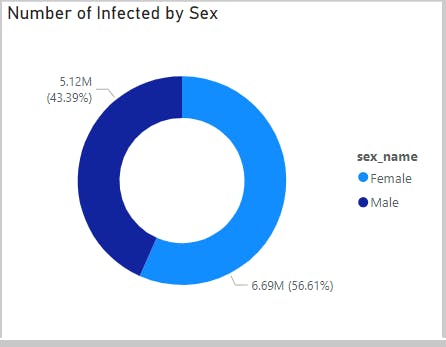
Analysis 5(Number of Infected by Sex)
This shows Females with the highest number of cases(6.69M, 56.61%) as compared to Males(5.12M, 43.39%)
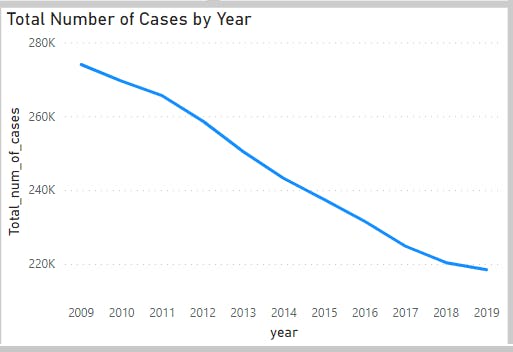
Analysis 6(Total Number of Cases by Year)
This analysis shows 2009 as the year with the highest number of cases and 2019 as the lowest(2009-2019)
HIV/AIDS INFECTION MONITORING DASHBOARD
Conclusion
This analysis helps us understand the trends across years of the HIV/AIDS diseases. We were able to monitor the impact and spread as well as effect of the diseases over the years based on population demographic. This gives data driven insights to help make reasonable conclusions as well as gives the health sector actionable insights and overview of the disease and its impact so far hereby improving better decision making.
References
vizhub.healthdata.org unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-a.. who.int/health-topics/hiv-aids
#dataanalytics #hivaidsinsightanalysis #bootcamp #hashnode @Ngsidehustle